OIDC Authentication
The DataHub React application supports OIDC authentication built on top of the Pac4j Play library. This enables operators of DataHub to integrate with 3rd party identity providers like Okta, Google, Keycloak, & more to authenticate their users.
1. Register an app with your Identity Provider
- Google Identity
- Okta
- Azure
Create a project in the Google API Console
Using an account linked to your organization, navigate to the Google API Console and select New project. Within this project, we will configure the OAuth2.0 screen and credentials.
Create OAuth2.0 consent screen
Navigate to OAuth consent screen. This is where you'll configure the screen your users see when attempting to log in to DataHub. Select Internal (if you only want your company users to have access) and then click Create. Note that in order to complete this step you should be logged into a Google account associated with your organization.
Fill out the details in the App Information & Domain sections. Make sure the 'Application Home Page' provided matches where DataHub is deployed at your organization. Once you've completed this, Save & Continue.
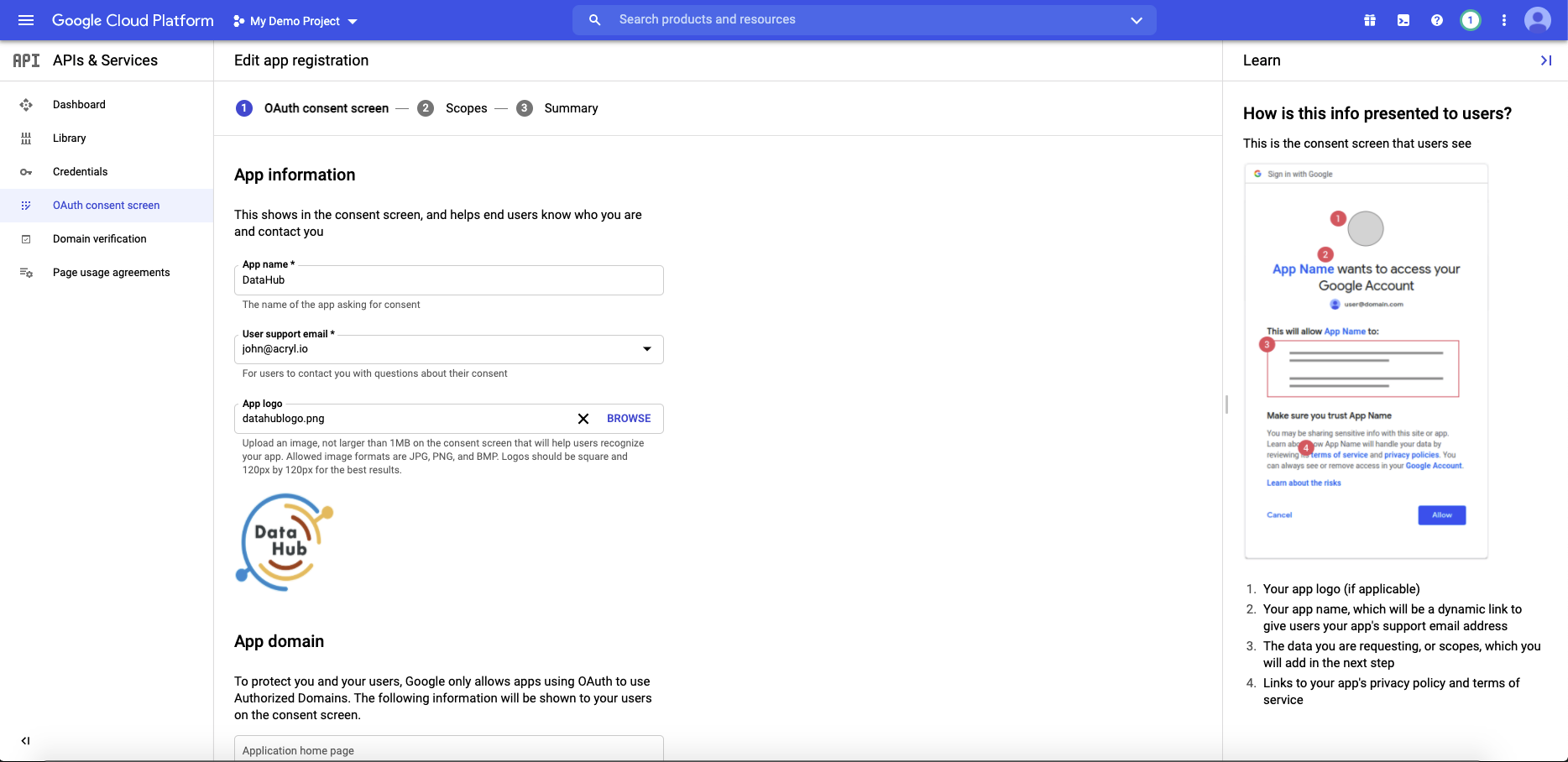
Configure the scopes
Next, click Add or Remove Scopes. Select the following scope and click Save & Continue.
- .../auth/userinfo.email
- .../auth/userinfo.profile
- openid
Create an application in Okta Developer Console
Log in to your Okta admin account & navigate to the developer console. Select Applications, then Add Application, the Create New App to create a new app.
Select Web as the Platform, and OpenID Connect as the Sign on method.
Click Create and name your application under General Settings and save.
- Login Redirect URI :
https://your-datahub-domain.com/callback/oidc. - Logout Redirect URI.
https://your-datahub-domain.com/login
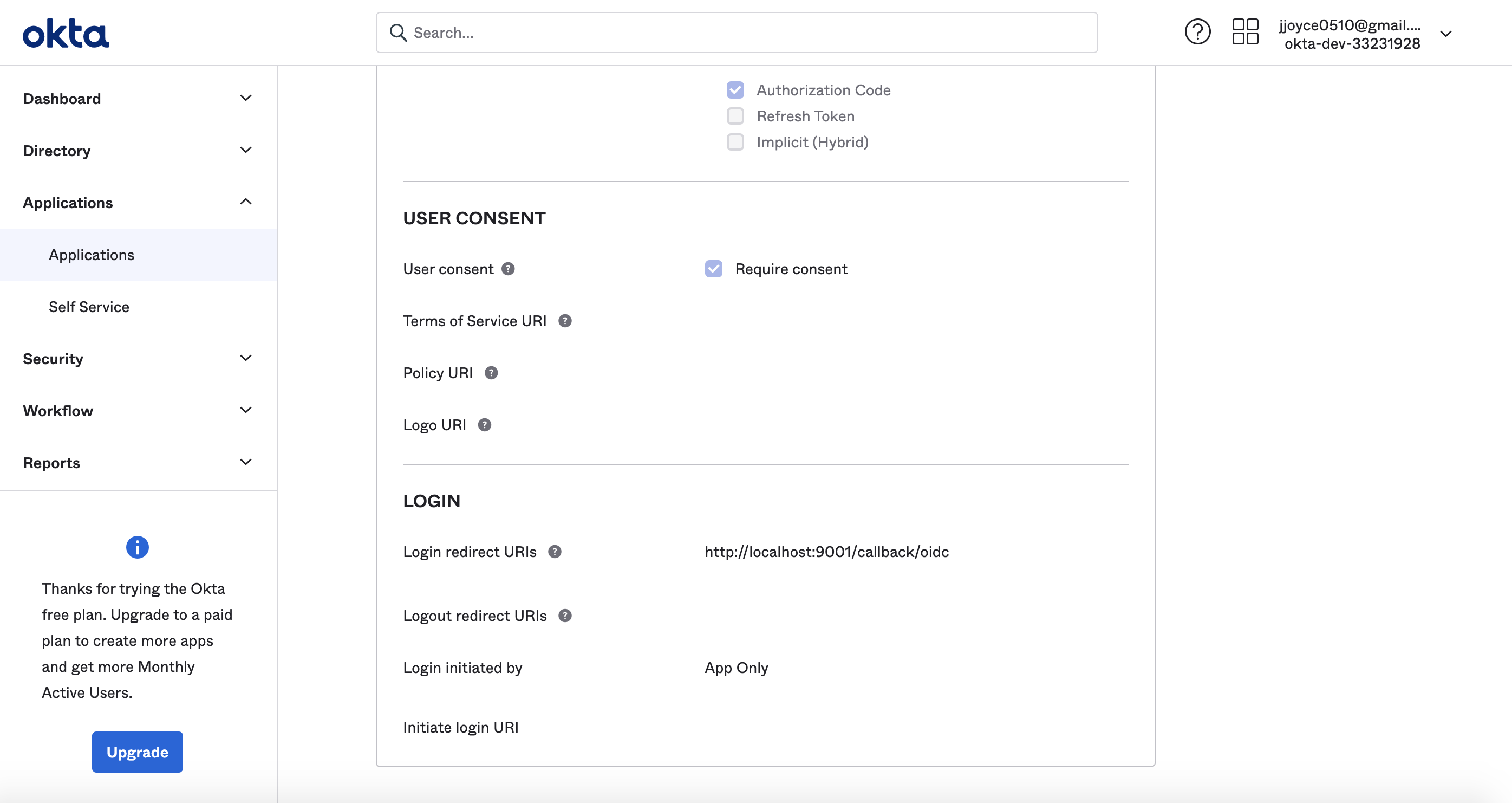
If you're enabling DataHub login as an Okta tile, you'll need to provide the Initiate Login URI. You
can set if to https://your-datahub-domain.com/authenticate. If you're just testing locally, this can be http://localhost:9002.
Create an application registration in Microsoft Azure portal
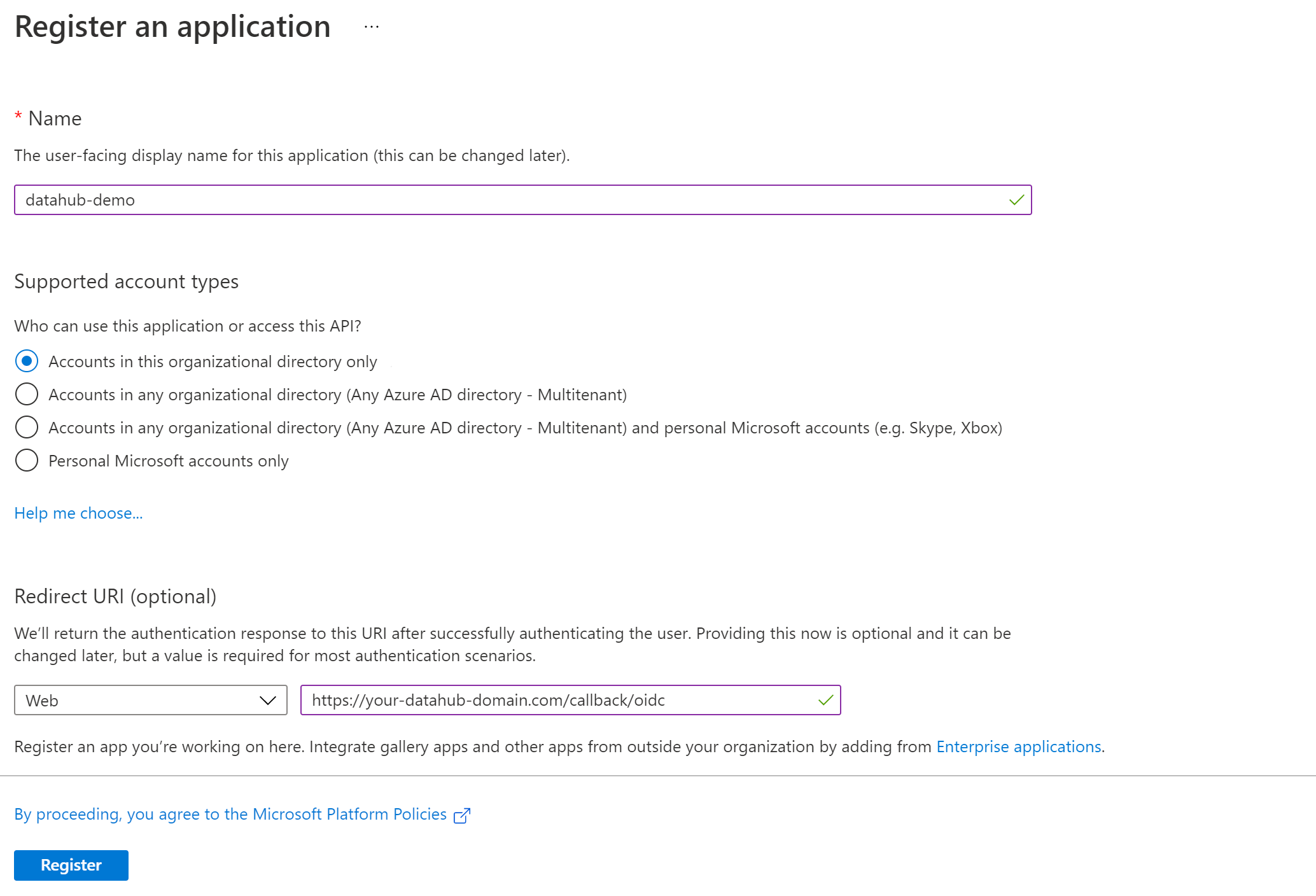
Using an account linked to your organization, navigate to the Microsoft Azure Portal. Select App registrations, then New registration to register a new app.
Name your app registration and choose who can access your application.
- Redirect URI : Select Web as type and enter
https://your-datahub-domain.com/callback/oidc
Azure supports more than one redirect URI, so both can be configured at the same time from the Authentication tab once the registration is complete. At this point, your app registration should look like the following. Finally, click Register.
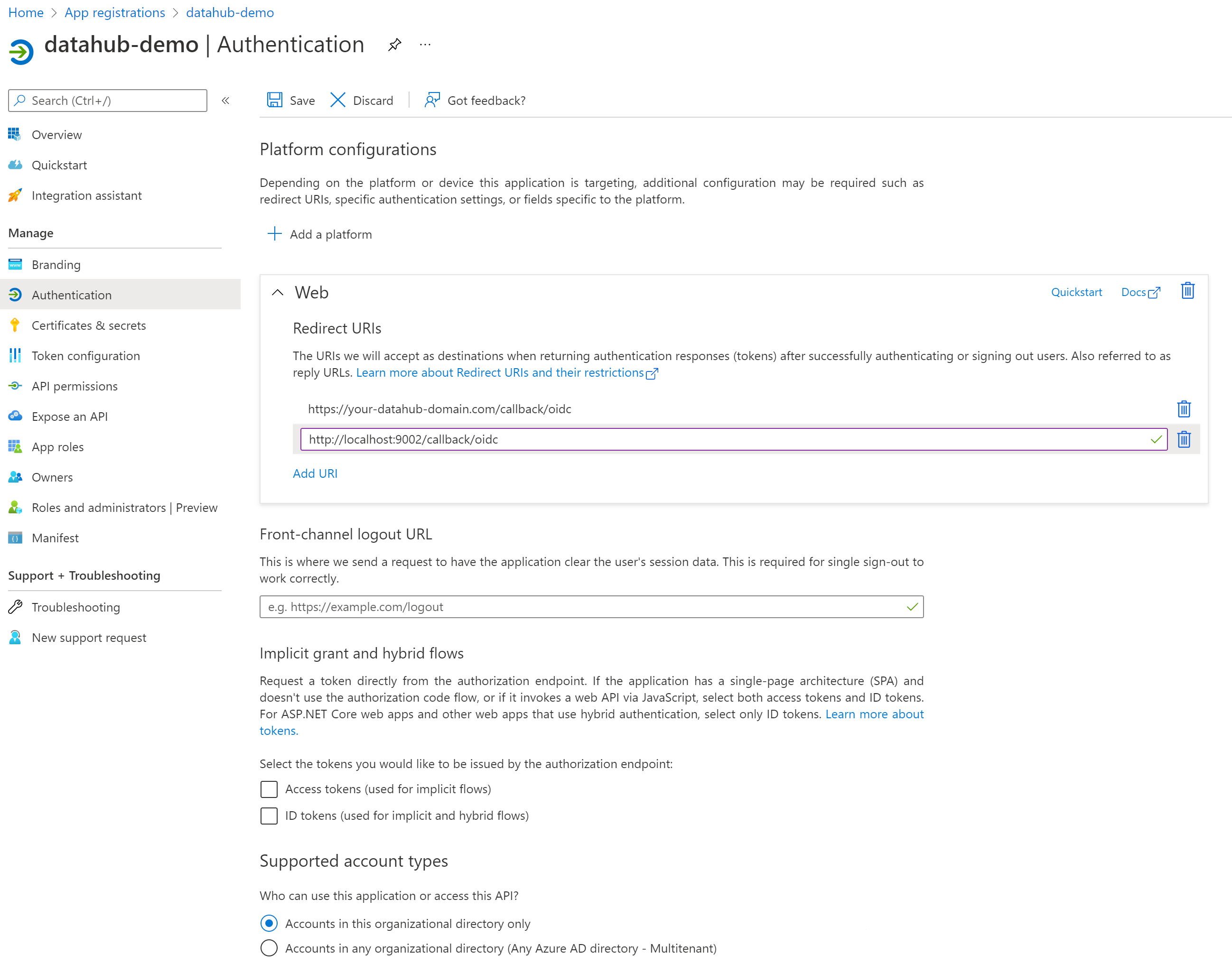
Once registration is done, you will land on the app registration Overview tab.
On the left-side navigation bar, click on Authentication under Manage and add extra redirect URIs if need be (if you want to support both local testing and Azure deployments). Finally, click Save.
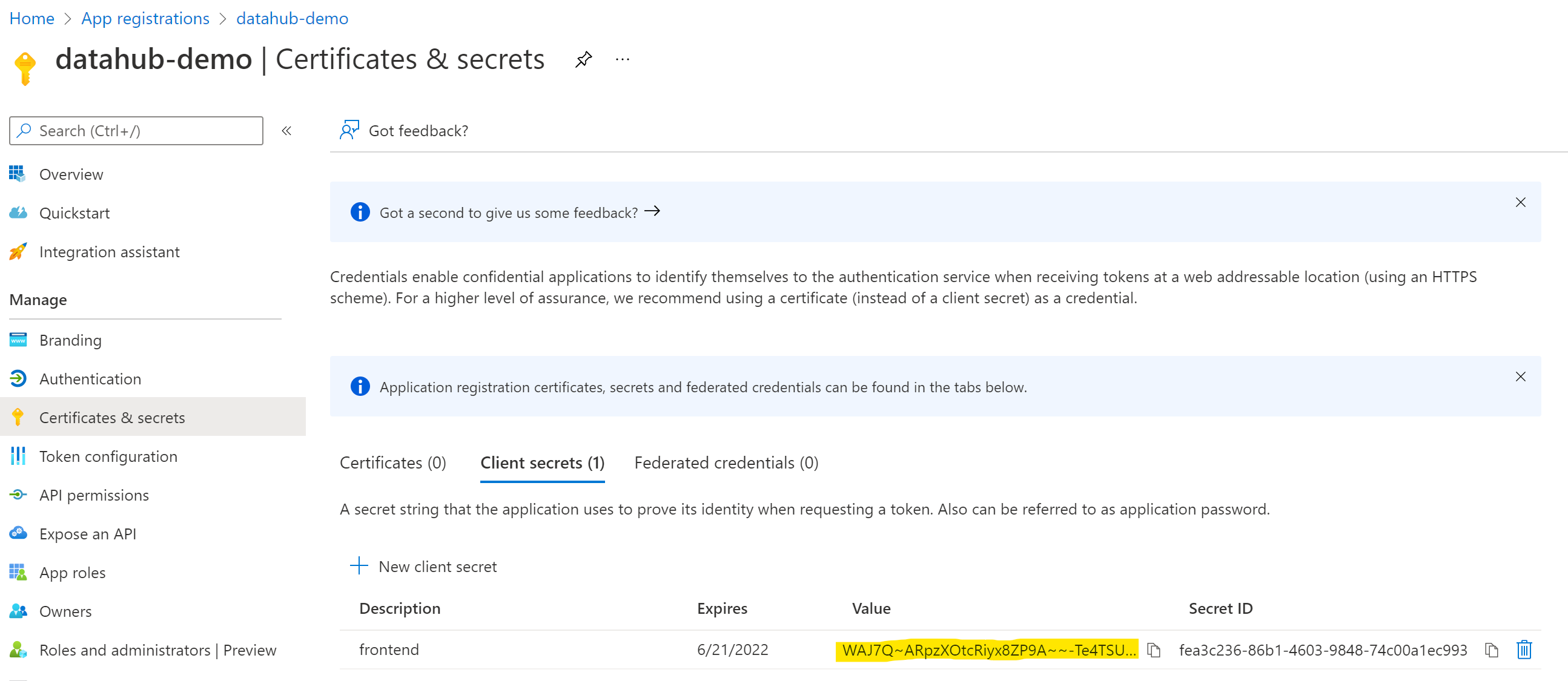
Configure Certificates & secrets
On the left-side navigation bar, click on Certificates & secrets under Manage.
Select Client secrets, then New client secret. Type in a meaningful description for your secret and select an expiry. Click the Add button when you are done.
Copy the value of your newly create secret since Azure will never display its value afterwards.
Configure API permissions
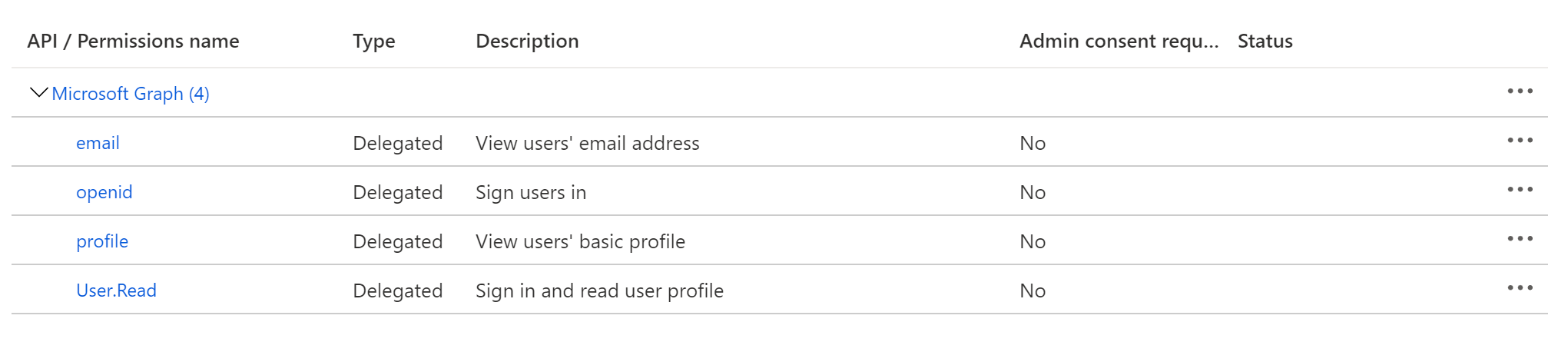
On the left-side navigation bar, click on API permissions under Manage. DataHub requires the following four Microsoft Graph APIs:
- User.Read (should be already configured)
- profile
- openid
Click on Add a permission, then from the Microsoft APIs tab select Microsoft Graph, then Delegated permissions. From the OpenId permissions category, select email, openid, profile and click Add permissions.
At this point, you should be looking at a screen like the following:
2. Obtain Client Credentials & Discovery URL
The goal of this step should be to obtain the following values, which will need to be configured before deploying DataHub:
- Client ID - A unique identifier for your application with the identity provider
- Client Secret - A shared secret to use for exchange between you and your identity provider
- Discovery URL - A URL where the OIDC API of your identity provider can be discovered. This should suffixed by
.well-known/openid-configuration. Sometimes, identity providers will not explicitly include this URL in their setup guides, though this endpoint will exist as per the OIDC specification. For more info see http://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-discovery-1_0.html.
- Google Identity
- Okta
- Azure
Obtain Client Credentials
Navigate to the Credentials tab. Click Create Credentials & select OAuth client ID as the credential type.
On the following screen, select Web application as your Application Type. Add the domain where DataHub is hosted to your 'Authorized Javascript Origins'.
https://your-datahub-domain.com
Add the domain where DataHub is hosted with the path /callback/oidc appended to 'Authorized Redirect URLs'. Finally, click Create
https://your-datahub-domain.com/callback/oidc
You will now receive a pair of values, a client id and a client secret. Bookmark these for the next step.
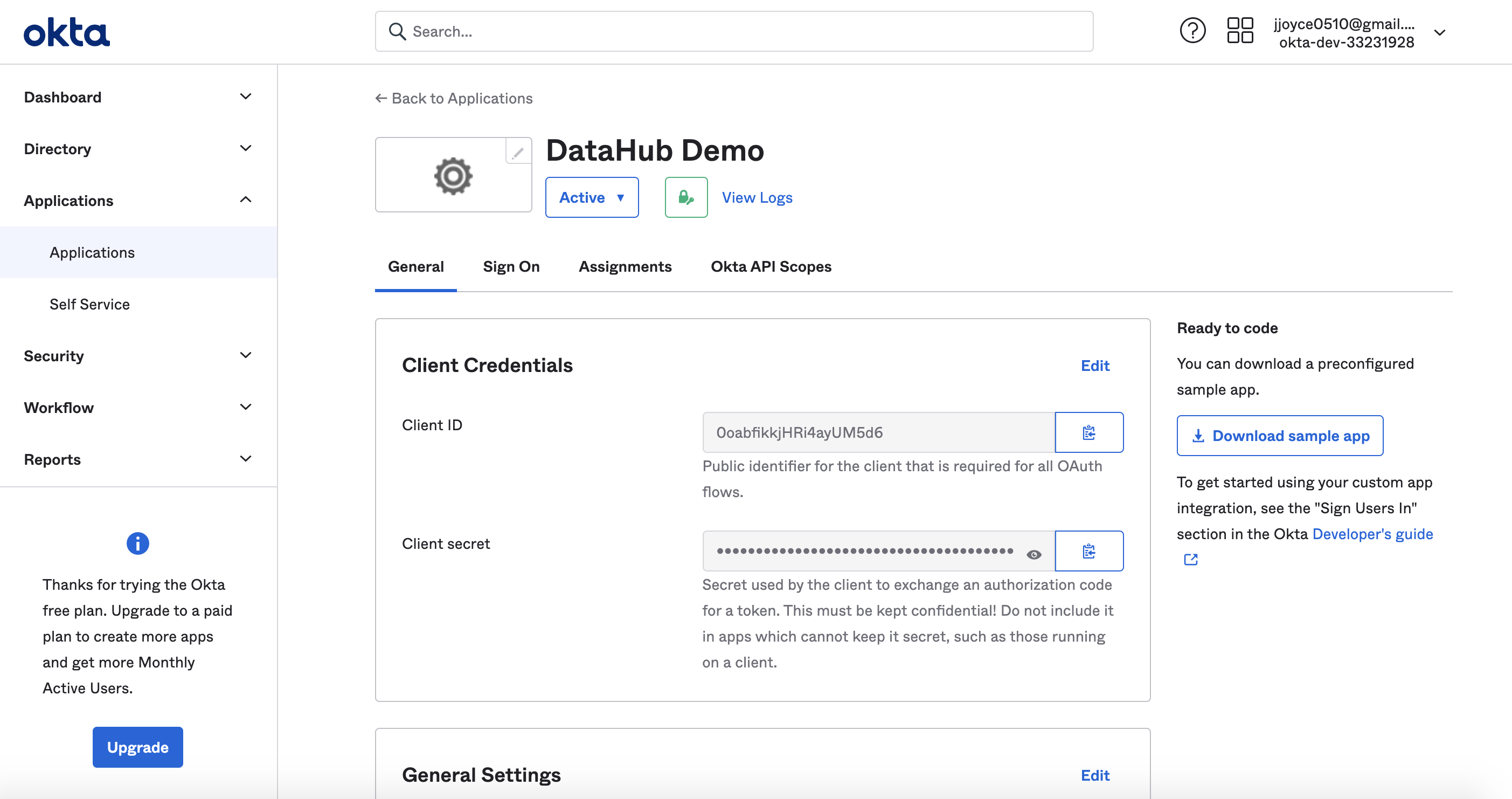
Obtain Client Credentials
After registering the app, you should see the client credentials. Bookmark the Client id and Client secret for the next step.
Obtain Discovery URI
On the same page, you should see an Okta Domain. Your OIDC discovery URI will be formatted as follows:
https://your-okta-domain.com/.well-known/openid-configuration
For example, https://dev-33231928.okta.com/.well-known/openid-configuration.
At this point, you should be looking at a screen like the following:
Obtain Application (Client) ID
On the left-side navigation bar, go back to the Overview tab. You should see the Application (client) ID. Save its value for the next step.
Obtain Discovery URI
On the same page, you should see a Directory (tenant) ID. Your OIDC discovery URI will be formatted as follows:
https://login.microsoftonline.com/{tenant ID}/v2.0/.well-known/openid-configuration
3. Configure DataHub Frontend Server
Docker
The next step to enabling OIDC involves configuring datahub-frontend to enable OIDC authentication with your Identity Provider.
To do so, you must update the datahub-frontend docker.env file with the
values received from your identity provider:
# Required Configuration Values:
AUTH_OIDC_ENABLED=true
AUTH_OIDC_CLIENT_ID=your-client-id
AUTH_OIDC_CLIENT_SECRET=your-client-secret
AUTH_OIDC_DISCOVERY_URI=your-provider-discovery-url
AUTH_OIDC_BASE_URL=your-datahub-url
| Configuration | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| AUTH_OIDC_ENABLED | Enable delegating authentication to OIDC identity provider | |
| AUTH_OIDC_CLIENT_ID | Unique client id received from identity provider | |
| AUTH_OIDC_CLIENT_SECRET | Unique client secret received from identity provider | |
| AUTH_OIDC_DISCOVERY_URI | Location of the identity provider OIDC discovery API. Suffixed with .well-known/openid-configuration | |
| AUTH_OIDC_BASE_URL | The base URL of your DataHub deployment, e.g. https://yourorgdatahub.com (prod) or http://localhost:9002 (testing) | |
| AUTH_SESSION_TTL_HOURS | The length of time in hours before a user will be prompted to login again. Controls the actor cookie expiration time in the browser. Numeric value converted to hours. | 24 |
| MAX_SESSION_TOKEN_AGE | Determines the expiration time of a session token. Session tokens are stateless so this determines at what time a session token may no longer be used and a valid session token can be used until this time has passed. Accepts a valid relative Java date style String. | 24h |
Providing these configs will cause DataHub to delegate authentication to your identity provider, requesting the "oidc email profile" scopes and parsing the "preferred_username" claim from the authenticated profile as the DataHub CorpUser identity.
By default, the login callback endpoint exposed by DataHub will be located at ${AUTH_OIDC_BASE_URL}/callback/oidc. This must exactly match the login redirect URL you've registered with your identity provider in step 1.
Kubernetes
In Kubernetes, you can add the above env variables in the values.yaml as follows.
datahub-frontend:
...
extraEnvs:
- name: AUTH_OIDC_ENABLED
value: "true"
- name: AUTH_OIDC_CLIENT_ID
value: your-client-id
- name: AUTH_OIDC_CLIENT_SECRET
value: your-client-secret
- name: AUTH_OIDC_DISCOVERY_URI
value: your-provider-discovery-url
- name: AUTH_OIDC_BASE_URL
value: your-datahub-url
You can also package OIDC client secrets into a k8s secret by running
kubectl create secret generic datahub-oidc-secret --from-literal=secret=<<OIDC SECRET>>
Then set the secret env as follows.
- name: AUTH_OIDC_CLIENT_SECRET
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: datahub-oidc-secret
key: secret
Advanced OIDC Configurations
You can optionally customize the flow further using advanced configurations. These allow you to specify the OIDC scopes requested, how the DataHub username is parsed from the claims returned by the identity provider, and how users and groups are extracted and provisioned from the OIDC claim set.
# Optional Configuration Values:
AUTH_OIDC_USER_NAME_CLAIM=your-custom-claim
AUTH_OIDC_USER_NAME_CLAIM_REGEX=your-custom-regex
AUTH_OIDC_SCOPE=your-custom-scope
AUTH_OIDC_CLIENT_AUTHENTICATION_METHOD=authentication-method
| Configuration | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| AUTH_OIDC_USER_NAME_CLAIM | The attribute that will contain the username used on the DataHub platform. By default, this is "email" providedas part of the standard email scope. | |
| AUTH_OIDC_USER_NAME_CLAIM_REGEX | A regex string used for extracting the username from the userNameClaim attribute. For example, if the userNameClaim field will contain an email address, and we want to omit the domain name suffix of the email, we can specify a customregex to do so. (e.g. ([^@]+)) | |
| AUTH_OIDC_SCOPE | A string representing the scopes to be requested from the identity provider, granted by the end user. For more info, see OpenID Connect Scopes. | |
| AUTH_OIDC_CLIENT_AUTHENTICATION_METHOD | a string representing the token authentication method to use with the identity provider. Default value is client_secret_basic, which uses HTTP Basic authentication. Another option is client_secret_post, which includes the client_id and secret_id as form parameters in the HTTP POST request. For more info, see OAuth 2.0 Client Authentication | client_secret_basic |
| AUTH_OIDC_PREFERRED_JWS_ALGORITHM | Can be used to select a preferred signing algorithm for id tokens. Examples include: RS256 or HS256. If your IdP includes none before RS256/HS256 in the list of signing algorithms, then this value MUST be set. |
User & Group Provisioning (JIT Provisioning)
By default, DataHub will optimistically attempt to provision users and groups that do not already exist at the time of login. For users, we extract information like first name, last name, display name, & email to construct a basic user profile. If a groups claim is present, we simply extract their names.
The default provisioning behavior can be customized using the following configs.
# User and groups provisioning
AUTH_OIDC_JIT_PROVISIONING_ENABLED=true
AUTH_OIDC_PRE_PROVISIONING_REQUIRED=false
AUTH_OIDC_EXTRACT_GROUPS_ENABLED=false
AUTH_OIDC_GROUPS_CLAIM=<your-groups-claim-name>
| Configuration | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
| AUTH_OIDC_JIT_PROVISIONING_ENABLED | Whether DataHub users & groups should be provisioned on login if they do not exist. | true |
| AUTH_OIDC_PRE_PROVISIONING_REQUIRED | Whether the user should already exist in DataHub when they login, failing login if they are not. This is appropriate for situations in which users and groups are batch ingested and tightly controlled inside your environment. | false |
| AUTH_OIDC_EXTRACT_GROUPS_ENABLED | Only applies if AUTH_OIDC_JIT_PROVISIONING_ENABLED is set to true. This determines whether we should attempt to extract a list of group names from a particular claim in the OIDC attributes. Note that if this is enabled, each login will re-sync group membership with the groups in your Identity Provider, clearing the group membership that has been assigned through the DataHub UI. Enable with care! | false |
| AUTH_OIDC_GROUPS_CLAIM | Only applies if AUTH_OIDC_EXTRACT_GROUPS_ENABLED is set to true. This determines which OIDC claims will contain a list of string group names. Accepts multiple claim names with comma-separated values. I.e: groups, teams, departments. | groups |
4. Restart datahub-frontend-react
Once configured, restarting the datahub-frontend-react container will enable an indirect authentication flow in which DataHub delegates authentication to the specified identity provider.
docker-compose -p datahub -f docker-compose.yml -f docker-compose.override.yml up datahub-frontend-react
Navigate to your DataHub domain to see SSO in action.
By default, enabling OIDC will not disable the dummy JAAS authentication path, which can be reached at the /login
route of the React app. To disable this authentication path, additionally specify the following config:
AUTH_JAAS_ENABLED=false
Summary
Once a user is authenticated by the identity provider, DataHub will extract a username from the provided claims and grant DataHub access to the user by setting a pair of session cookies.
A brief summary of the steps that occur when the user navigates to the React app are as follows:
- A
GETto the/authenticateendpoint indatahub-frontendserver is initiated - The
/authenticateattempts to authenticate the request via session cookies - If auth fails, the server issues a redirect to the Identity Provider's login experience
- The user logs in with the Identity Provider
- The Identity Provider authenticates the user and redirects back to DataHub's registered login redirect URL, providing an authorization code which can be used to retrieve information on behalf of the authenticated user
- DataHub fetches the authenticated user's profile and extracts a username to identify the user on DataHub (eg. urn:li:corpuser:username)
- DataHub sets session cookies for the newly authenticated user
- DataHub redirects the user to the homepage ("/")
Troubleshooting
No users can log in. Instead, I get redirected to the login page with an error. What do I do?
This can occur for a variety of reasons, but most often it is due to misconfiguration of Single-Sign On, either on the DataHub side or on the Identity Provider side.
- Verify that all values are consistent across them (e.g. the host URL where DataHub is deployed), and that no values are misspelled (client id, client secret).
- Verify that the scopes requested are supported by your Identity Provider and that the claim (i.e. attribute) DataHub uses for uniquely identifying the user is supported by your Identity Provider (refer to Identity Provider OpenID Connect documentation). By default, this claim is
email. - Make sure the Discovery URI you've configured (
AUTH_OIDC_DISCOVERY_URI) is accessible where the datahub-frontend container is running. You can do this by issuing a basic CURL to the address (Pro-Tip: you may also visit the address in your browser to check more specific details about your Identity Provider). - Check the container logs for the
datahub-frontendcontainer. This should hopefully provide some additional context around why exactly the login handoff is not working.
If all else fails, feel free to reach out to the DataHub Community on Slack for real-time support.
I'm seeing an error in the `datahub-frontend` logs when a user tries to login: Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException: Failed to resolve user name claim from profile provided by Identity Provider. Missing attribute. Attribute: 'email', Regex: '(.*)', Profile: { ....
This indicates that your Identity Provider does not provide the claim with name 'email', which DataHub uses by default to uniquely identify users within your organization.
To fix this, you may need to
- Change the claim that is used as the unique user identifier to something else by changing the
AUTH_OIDC_USER_NAME_CLAIM(e.g. to "name" or "preferredusername") _OR - Change the environment variable
AUTH_OIDC_SCOPEto include the scope required to retrieve the claim with name "email"
For the datahub-frontend container / pod.
Reference
Check the documentation for your Identity Provider to learn more about the scope claims supported.
